Rebuilding the master database is done using the Rebuild Master utility "rebuildm.exe" which is located in the 80\Tools\Binn directory of the SQL Server installation CD or Folder.
Select the server and instance that you want to rebuild. Now you need access to the files from the install CD for SQL Server. Browse to the Data dircetory in the SQL Server install files. Set the collation you want SQL Server to be using, and hit Rebuild.
If you are run the utility using the CD as the source, you might encounter the error:
Rebuild Master failed with error -1
Microsoft Support Q273572 lists the error as a bug in the utility. As it copies the read-only files from the install CD it does not turn off the read-only flag. To work around this simply copy the Data directory from the CD to the harddrive and turn off the read-only setting for the files. Then go ahead and rebuild again.
Once the master database is rebuilt, verify that it worked by starting SQL Server. The instance should start, but all the previous settings and databases will be missing. Restoring the Master database will bring back all the previous instance settings.
My Journey with Microsoft SQL Server as SQL Server DBA!
Stories on Issues Faced, Struggled, Hacked, Profiled, Troubleshooted, Resolved, Fixed and .... Restarted!
Showing posts with label SQL 2000. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SQL 2000. Show all posts
Wednesday, October 22, 2008
SQL Server Dead Locks - How to Resolve?
I will be updating this post on the details which I know about SQL Server Dead locks...
What is a deadlock?
A deadlock occurs when two system server process IDs (SPIDs) are waiting for a resource and neither process can advance because the other process is preventing it from getting the resource.
How SQL Server will handle DeadlockThe lock manager’s thread checks for deadlocks. When a lock manager’s deadlock detection algorithm detects a deadlock, the lock manager chooses one of the SPIDs as a victim (This will be the SPID which consumes least resources). The lock manager initiates a 1205 error message that is sent to the client, and the lock manager kills the SPID. Killing the SPID frees the resources and allows the other SPID to continue. Killing the SPID that is the deadlock victim is what causes the broken connection that the Visual Basic front-end application experiences.
In a well designed application, the front-end application should trap for the 1205 error, reconnect to SQL Server, and then re-submit the transaction.
Although deadlocks can be minimized, they cannot be completely avoided. That is why the front-end application should be designed to handle deadlocks.
How to identify a deadlock
Enable below trace commands which will help capturing details about deadlock
dbcc traceon (1204, 3605, -1)
go
dbcc tracestatus(-1)
go
Explanation:
The "-1" indicates all SPIDs.
Also instead of 1204 you can also use 1205. Below are the difference between them
The 1204 parameter collects information about the process and the resources when the deadlock detection algorithm encounters a deadlock. The 3605 parameter writes this information to the SQL Server error logs.
The 1205 startup parameter collects information every time that the deadlock algorithm checks for a deadlock, not when a deadlock is encountered.
Now run the SQL Profiler by selecting lock event for "deadlock" and for "deadlock chain." "Deadlock" corresponds to the -T1204 flag, and "deadlock chain" corresponds to the -T1205 flag which will give the complete SQL Statements creating DeadLock.
How to set priority for SPID so that SQL Server will KILL it accordingly
SET DEADLOCK_PRIORITY { LOW NORMAL @deadlock_var }
Explanation:
Low tells SQL Server that the current session should be the preferred deadlock victim, not the session that incurs the least amount of rollback resources. The standard deadlock error message 1205 is returned.
Normal tells SQL Server to use the default deadlock method.
@deadlock_var is a character variable specifying which deadlock method you want to use. Specify "3" for low, or "6" for normal.
This command is set a runtime for a specified user connection
What will be the Error Code?
1205 will be error message!
Some Links
1. http://www.sql-server-performance.com/tips/deadlocks_p1.aspx (Brad McGehee)
2. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/832524 (Microsoft KB)
3. sqlservercentral.com/tracingdeadlocks/1324/ (Forum Artcile)
What is a deadlock?
A deadlock occurs when two system server process IDs (SPIDs) are waiting for a resource and neither process can advance because the other process is preventing it from getting the resource.
How SQL Server will handle DeadlockThe lock manager’s thread checks for deadlocks. When a lock manager’s deadlock detection algorithm detects a deadlock, the lock manager chooses one of the SPIDs as a victim (This will be the SPID which consumes least resources). The lock manager initiates a 1205 error message that is sent to the client, and the lock manager kills the SPID. Killing the SPID frees the resources and allows the other SPID to continue. Killing the SPID that is the deadlock victim is what causes the broken connection that the Visual Basic front-end application experiences.
In a well designed application, the front-end application should trap for the 1205 error, reconnect to SQL Server, and then re-submit the transaction.
Although deadlocks can be minimized, they cannot be completely avoided. That is why the front-end application should be designed to handle deadlocks.
How to identify a deadlock
Enable below trace commands which will help capturing details about deadlock
dbcc traceon (1204, 3605, -1)
go
dbcc tracestatus(-1)
go
Explanation:
The "-1" indicates all SPIDs.
Also instead of 1204 you can also use 1205. Below are the difference between them
The 1204 parameter collects information about the process and the resources when the deadlock detection algorithm encounters a deadlock. The 3605 parameter writes this information to the SQL Server error logs.
The 1205 startup parameter collects information every time that the deadlock algorithm checks for a deadlock, not when a deadlock is encountered.
Now run the SQL Profiler by selecting lock event for "deadlock" and for "deadlock chain." "Deadlock" corresponds to the -T1204 flag, and "deadlock chain" corresponds to the -T1205 flag which will give the complete SQL Statements creating DeadLock.
How to set priority for SPID so that SQL Server will KILL it accordingly
SET DEADLOCK_PRIORITY { LOW NORMAL @deadlock_var }
Explanation:
Low tells SQL Server that the current session should be the preferred deadlock victim, not the session that incurs the least amount of rollback resources. The standard deadlock error message 1205 is returned.
Normal tells SQL Server to use the default deadlock method.
@deadlock_var is a character variable specifying which deadlock method you want to use. Specify "3" for low, or "6" for normal.
This command is set a runtime for a specified user connection
What will be the Error Code?
1205 will be error message!
Some Links
1. http://www.sql-server-performance.com/tips/deadlocks_p1.aspx (Brad McGehee)
2. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/832524 (Microsoft KB)
3. sqlservercentral.com/tracingdeadlocks/1324/ (Forum Artcile)
Tuesday, October 21, 2008
How to delete Full text catalog after restoring database!
When we are not copying the Full Text Catalog to new Server but we are restoring database to new server then there is only one choice to drop the full text catalog.
When we try to do that we will encounter following error
Error 7605: Full-text catalog has been lost after restoring database to new server
Error 7605: Full-text catalog 'ABCD' has been lost. Use sp_fulltext_catalog to rebuild and to repopulate this full-text catalog.
So the only solution to this is run following commands on order specified and then later we will be able to drop and recreate the catalog and start new population.
USE [dBName]
sp_fulltext_database 'disable'
Go
sp_fulltext_service 'clean_up'
Go
sp_fulltext_database 'enable'
Go
These commands will reset the entire system. Theoretically, you should be able to rebuild then.
When we try to do that we will encounter following error
Error 7605: Full-text catalog has been lost after restoring database to new server
Error 7605: Full-text catalog 'ABCD' has been lost. Use sp_fulltext_catalog to rebuild and to repopulate this full-text catalog.
So the only solution to this is run following commands on order specified and then later we will be able to drop and recreate the catalog and start new population.
USE [dBName]
sp_fulltext_database 'disable'
Go
sp_fulltext_service 'clean_up'
Go
sp_fulltext_database 'enable'
Go
These commands will reset the entire system. Theoretically, you should be able to rebuild then.
Monitor Linked Server in SQL 2000
Since there are no scripts available in net for monitoring Linked Servers, I wrote a script and published in SQLServerCentral.com. You can check the article from this link for detailed report on the script. Also I have published the script below for immediate usage!
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Name : uspMonitor_LinkedServer
--- Author : Sakthi
--- Release Date : 05/03/2008
--- Revision : O
--- Revision History:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ALTER PROCEDURE dbo.[uspMonitor_LinkedServer]
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @ServerName VARCHAR(255)
DECLARE @ServerType VARCHAR(50)
DECLARE @Dummy VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE @msg VARCHAR(500)
DECLARE @hr INT
DECLARE @sql INT
DECLARE @Error bigint
DECLARE @status INT ;SET @status = 0
-- Get the list of Excel and Access Linked Servers Since the Testing Method is different here
DECLARE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR
SELECT srvname FROM master..sysservers WHERE isremote=1 AND srvproduct NOT LIKE 'SQL Server%' AND srvname NOT IN ('')
OPEN Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Reading a sample Table Name to Dummy Variable from Excel sheet to ensure Connectivity
SELECT TOP 1 @Dummy = TABLE_NAME from master.dbo.SYSREMOTE_TABLES (@ServerName)
-- Checking Status and Sending Alert Mail to Team
IF @@ROWCOUNT = 0 BEGIN
SET @msg= 'Error in Getting Data from linked server ' + @ServerName + ' Configured at ' + @@SERVERNAME
Exec [MONITOR].master.dbo.xp_smtp_sendmail @from= 'Linked_Server_Alert@Company.com' ,@from_name= @@SERVERNAME ,
@to='Team@Company.com',
@priority = 'HIGH', @subject=@msg,
@type= 'text/plain', @server = 'mailserver.company.com'
Print 'Mail Sent' + @ServerName
END
SET @status = 0 -- Setting the Status Variable back to 0 for Resetting Error Trapped
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
END
CLOSE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
DEALLOCATE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
-- Get the list of SQL Linked Servers Since the Testing Method is different here
DECLARE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR
SELECT srvname FROM master..sysservers WHERE isremote=1 AND srvproduct LIKE 'SQL Server%' AND srvname NOT IN ('')
OPEN Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Performing a login and check the status of Server(SQL) to ensure Connectivity
EXEC @hr = sp_OACreate 'SQLDMO.SQLServer', @sql OUTPUT
---IF @hr<>0 EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @sql -- Used while testing procedure to check error msg
EXEC @hr = sp_OASetProperty @sql ,'LoginSecure','True'
EXEC @hr = sp_OASetProperty @sql ,'LoginTimeout',10
EXEC @hr = sp_OAMethod @sql,'Connect',null,@ServerName
EXEC @hr = sp_OAGetProperty @sql ,'Status',@status OUTPUT
EXEC @hr = sp_OAMethod @sql,'DisConnect',null
EXEC @hr = sp_OADestroy @sql
-- Checking Status and Sending Alert Mail to Team
IF @status <> 1 BEGIN
SET @msg= 'Timeout in Getting Data from linked server ' + @ServerName + ' Configured at ' + @@SERVERNAME
Exec [MONITOR].master.dbo.xp_smtp_sendmail @from= 'Linked_Server_Alert@Company.com' ,@from_name= @@SERVERNAME ,
@to='Team@Company.com',
@priority = 'HIGH', @subject=@msg,
@type= 'text/plain', @server = 'mailserver.company.com'
Print 'Mail Sent' + @ServerName
END
print @status
SET @status = 0 -- Setting the Status Variable back to 0 for Resetting Error Trapped
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
END
CLOSE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
DEALLOCATE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
END
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Name : uspMonitor_LinkedServer
--- Author : Sakthi
--- Release Date : 05/03/2008
--- Revision : O
--- Revision History:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ALTER PROCEDURE dbo.[uspMonitor_LinkedServer]
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @ServerName VARCHAR(255)
DECLARE @ServerType VARCHAR(50)
DECLARE @Dummy VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE @msg VARCHAR(500)
DECLARE @hr INT
DECLARE @sql INT
DECLARE @Error bigint
DECLARE @status INT ;SET @status = 0
-- Get the list of Excel and Access Linked Servers Since the Testing Method is different here
DECLARE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR
SELECT srvname FROM master..sysservers WHERE isremote=1 AND srvproduct NOT LIKE 'SQL Server%' AND srvname NOT IN ('')
OPEN Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Reading a sample Table Name to Dummy Variable from Excel sheet to ensure Connectivity
SELECT TOP 1 @Dummy = TABLE_NAME from master.dbo.SYSREMOTE_TABLES (@ServerName)
-- Checking Status and Sending Alert Mail to Team
IF @@ROWCOUNT = 0 BEGIN
SET @msg= 'Error in Getting Data from linked server ' + @ServerName + ' Configured at ' + @@SERVERNAME
Exec [MONITOR].master.dbo.xp_smtp_sendmail @from= 'Linked_Server_Alert@Company.com' ,@from_name= @@SERVERNAME ,
@to='Team@Company.com',
@priority = 'HIGH', @subject=@msg,
@type= 'text/plain', @server = 'mailserver.company.com'
Print 'Mail Sent' + @ServerName
END
SET @status = 0 -- Setting the Status Variable back to 0 for Resetting Error Trapped
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
END
CLOSE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
DEALLOCATE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
-- Get the list of SQL Linked Servers Since the Testing Method is different here
DECLARE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr CURSOR FAST_FORWARD FOR
SELECT srvname FROM master..sysservers WHERE isremote=1 AND srvproduct LIKE 'SQL Server%' AND srvname NOT IN ('')
OPEN Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Performing a login and check the status of Server(SQL) to ensure Connectivity
EXEC @hr = sp_OACreate 'SQLDMO.SQLServer', @sql OUTPUT
---IF @hr<>0 EXEC sp_OAGetErrorInfo @sql -- Used while testing procedure to check error msg
EXEC @hr = sp_OASetProperty @sql ,'LoginSecure','True'
EXEC @hr = sp_OASetProperty @sql ,'LoginTimeout',10
EXEC @hr = sp_OAMethod @sql,'Connect',null,@ServerName
EXEC @hr = sp_OAGetProperty @sql ,'Status',@status OUTPUT
EXEC @hr = sp_OAMethod @sql,'DisConnect',null
EXEC @hr = sp_OADestroy @sql
-- Checking Status and Sending Alert Mail to Team
IF @status <> 1 BEGIN
SET @msg= 'Timeout in Getting Data from linked server ' + @ServerName + ' Configured at ' + @@SERVERNAME
Exec [MONITOR].master.dbo.xp_smtp_sendmail @from= 'Linked_Server_Alert@Company.com' ,@from_name= @@SERVERNAME ,
@to='Team@Company.com',
@priority = 'HIGH', @subject=@msg,
@type= 'text/plain', @server = 'mailserver.company.com'
Print 'Mail Sent' + @ServerName
END
print @status
SET @status = 0 -- Setting the Status Variable back to 0 for Resetting Error Trapped
FETCH NEXT FROM Lnkd_srvr_Crsr INTO @ServerName
END
CLOSE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
DEALLOCATE Lnkd_srvr_Crsr
END
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SQL 2000 SP4 Upgradation Error - Error running script: sp3_serv_uni.sql (1)
First of all, I want to let you know that when you are upgrading SQL Server 2000 to SP4, make sure that you are Stopping and Changing startup type to Manual for below Services
1. MSSQL$Instance
2. Windows Management Instrumentation
3. Microsoft Search
4. SQLAgent$Instance
If you perform the above steps then you will never face issue while upgradation.
Incase you get below error "Error running script: sp3_serv_uni.sql (1)" then solution is to rename dbmslpcn.dll in C:\Windows\system32 and run setup so that dll will be created automatically.

1. MSSQL$Instance
2. Windows Management Instrumentation
3. Microsoft Search
4. SQLAgent$Instance
If you perform the above steps then you will never face issue while upgradation.
Incase you get below error "Error running script: sp3_serv_uni.sql (1)" then solution is to rename dbmslpcn.dll in C:\Windows\system32 and run setup so that dll will be created automatically.

Execution of a full-text operation failed. A clause of the query contained only ignored words
We faced this issue of jobs started failing after upgrading from Windows 2000 to Windows 2003. To be precise a particluar statement is failing and when ran the statement in SSMS, the following error occurs
Server: Msg 7619, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 Execution of a full-text operation failed. A clause of the query contained only ignored words.
Root Cause:
This issue is happenning due to a deliberate change in the behaviour in "&" and other language breakers. This was done to take of other serious Issues which were caused in SQL 2000. The file which has this change incorporated is langwrbk.dll.
Resolution:
Though there is no solution for this issue, the workaround to this problem would be
1) Go back to Windows Server 2000
2) Change the way the words are stored (For Example AT&T can be stored as ATT)
3) Remove entries from Noise words which are causing this error (Can be found in the Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL$Instance\FTDATA\SQLServer$Instance\Config)
4) Use FREETEXT instead of CONTAINS, but this might also return non-relevant information, which might not be acceptable.
In Conclusion:
Unfortunately there is nothing that Microsoft can do to change this, since this was a deliberate change made in the way Language Breakers behave in Windows 2003. So the new dll used in Windows 2003 is langwrbk.dll. This change was made, because the previous behaviour With the language breakers had many different issues.
Some useful links for your reference.
295772 How to debug full-text search when a 7608 (0x80004005) error message occurs in SQL Server
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;295772
889708 The full-text search results that are returned in a clustered SQL Server 2000 environment may be different when the active node changes
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;889708
905617 SQL Server 2005 full-text search includes improved and updated noise word files
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;905617
Server: Msg 7619, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 Execution of a full-text operation failed. A clause of the query contained only ignored words.
Root Cause:
This issue is happenning due to a deliberate change in the behaviour in "&" and other language breakers. This was done to take of other serious Issues which were caused in SQL 2000. The file which has this change incorporated is langwrbk.dll.
Resolution:
Though there is no solution for this issue, the workaround to this problem would be
1) Go back to Windows Server 2000
2) Change the way the words are stored (For Example AT&T can be stored as ATT)
3) Remove entries from Noise words which are causing this error (Can be found in the Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL$Instance\FTDATA\SQLServer$Instance\Config)
4) Use FREETEXT instead of CONTAINS, but this might also return non-relevant information, which might not be acceptable.
In Conclusion:
Unfortunately there is nothing that Microsoft can do to change this, since this was a deliberate change made in the way Language Breakers behave in Windows 2003. So the new dll used in Windows 2003 is langwrbk.dll. This change was made, because the previous behaviour With the language breakers had many different issues.
Some useful links for your reference.
295772 How to debug full-text search when a 7608 (0x80004005) error message occurs in SQL Server
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;295772
889708 The full-text search results that are returned in a clustered SQL Server 2000 environment may be different when the active node changes
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;889708
905617 SQL Server 2005 full-text search includes improved and updated noise word files
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;905617
Run Job During IDLE CPU Condition
 Have you ever tried this option?
Have you ever tried this option?SQL Server Agent has an option to schedule a job to run when CPU(s) become idle, this can be a good choice for jobs which need more resources!
For example, You Server may be fully busy during USA and UK business hours and may be idle during the remaining time, so in that case we cannot define the exact period for the job but if we choose this option then SQL Server will automatically run the job when CPU become's IDLE.
On the other side you may get doubt that "incase CPU's are idle for just 2 mins during peak time, this schedule will start and may add to the utilization!"... Don't worry, Explan Enterprise Manager --> Go to SQL Server Agent --> Right click --> Select Properties --> Select Advanced Tab you will find below option

Here you can specify your own criteria for what is so called "IDLE" condition and only if this criteria is met then SQL Server Agent will run those jobs scheduled for IDLE CPU condition!
Test it and implement on exact fit situation!
Saturday, October 18, 2008
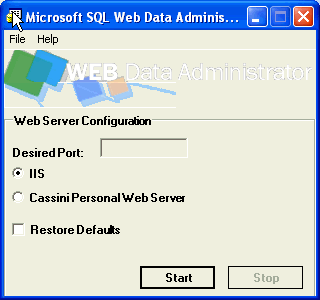
Web Based SQL Database Administration Tool From Microsoft
This is a web based application that can be installed on a web server in your environment to manage your SQL Servers over internet or intranet.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)